Cybersecurity Basics: The Data Security Lifecycle
📘 Essential for anyone preparing for the ISC2 CC exam
Hello everyone,
Let’s take a look at another cybersecurity topic that you need to be familiar with to pass the CC(Certified in Cybersecurity) exam.
Why the Data Security Lifecycle Matters?
Cybersecurity isn’t just about penetration testing and cryptography...
It’s about protecting data at every stage of its journey.
From the moment it’s created to the day it’s deleted, data is constantly moving, being stored, shared, and processed. And every stage opens up new risks.
If you don’t understand how data flows through its lifecycle, you can’t protect it effectively. That’s why the Data Security Lifecycle is crucial, as it helps security professionals identify where sensitive information lives, how it's handled, and where it might be exposed.
Lucky for you, I can explain it to you in simple terms!
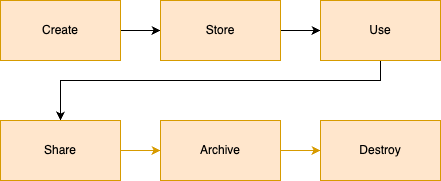
There are 6 stages of the data security lifecycle. Each one of them is equally important and needs to be handled accordingly. Failing in any of these stages could cause serious trouble.
Let’s break it down step by step👇
🔁 1. Create
What happens: Data is generated or acquired.
Example: A user fills out a web form.
Security tip: Classify the data based on sensitivity (e.g., public, internal, confidential).
🗃️ 2. Store
What happens: Data is saved on a device or in the cloud.
Example: A database stores customer records.
Security tip: Encrypt the data at rest and restrict access using permissions.
🧠 3. Use
What happens: Data is accessed or processed.
Example: An employee views a customer profile.
Security tip: Apply the principle of least privilege, monitor user activity.
🌐 4. Share / Transmit
What happens: Data is moved from one location or person to another.
Example: Sending an email with an attachment.
Security tip: Encrypt data in transit (e.g., HTTPS, VPNs).
📦 5. Archive
What happens: Data is stored long-term but rarely accessed.
Example: Backups or compliance records.
Security tip: Apply retention policies, restrict access, and encrypt archived data.
🗑️ 6. Destroy
What happens: Data is permanently deleted.
Example: Wiping an old hard drive.
Security tip: Use secure deletion methods to prevent recovery (e.g., shredding, overwriting).
The good news is that this lifecycle applies to ALL data. However, each phase could look very different based on the data type you’re dealing with.
Conclusion
Understanding the data security lifecycle is crucial for any cybersecurity specialist. Especially if you’re new to this field, you need to understand that it’s not just about penetration testing and encryption. Cybersecurity is much more about concepts and solutions, and like it or not, data is one of the most important assets for most businesses and individuals.
If you want to protect it effectively, you need to understand how it flows, where it lives, and where it's vulnerable. And that starts with the Data Security Lifecycle.
📩 Subscribe to my Patreon for free so you won’t miss the next posts. Especially if you’re just starting your journey into cybersecurity!